Why Cybersecurity, In today’s rapidly growing digital economy, protecting economic data is more important than ever. As online banking, digital wallets and fintech services increase, there is a risk of cyber-attacks. From identity theft to a large-scale scam, financial institutions must face constant threats that require strong, smart security.
Take this example: Late Night, a bank manager receives warnings about suspicious activity in a larger account. At the same time, millions of customers find that their personal information has been stolen overnight. It may look like a movie, but it’s a reality in front of banks and fintech companies all over the world.
According to the World Economic Forum, about 20% of all cyber events have targeted the financial sector over the last 20 years, resulting in a direct loss of around $ 12 billion. These attacks do not only harm businesses – they damage customers, disrupt the markets and threaten the general stability of economic systems.
With cyber dangers growing every year, cyber security has become the backbone of financial security. This is no longer a technical alternative – it is a strategic requirement for the protection of money, data and belief in the digital age.
Cybersecurity in finance: trends and threats
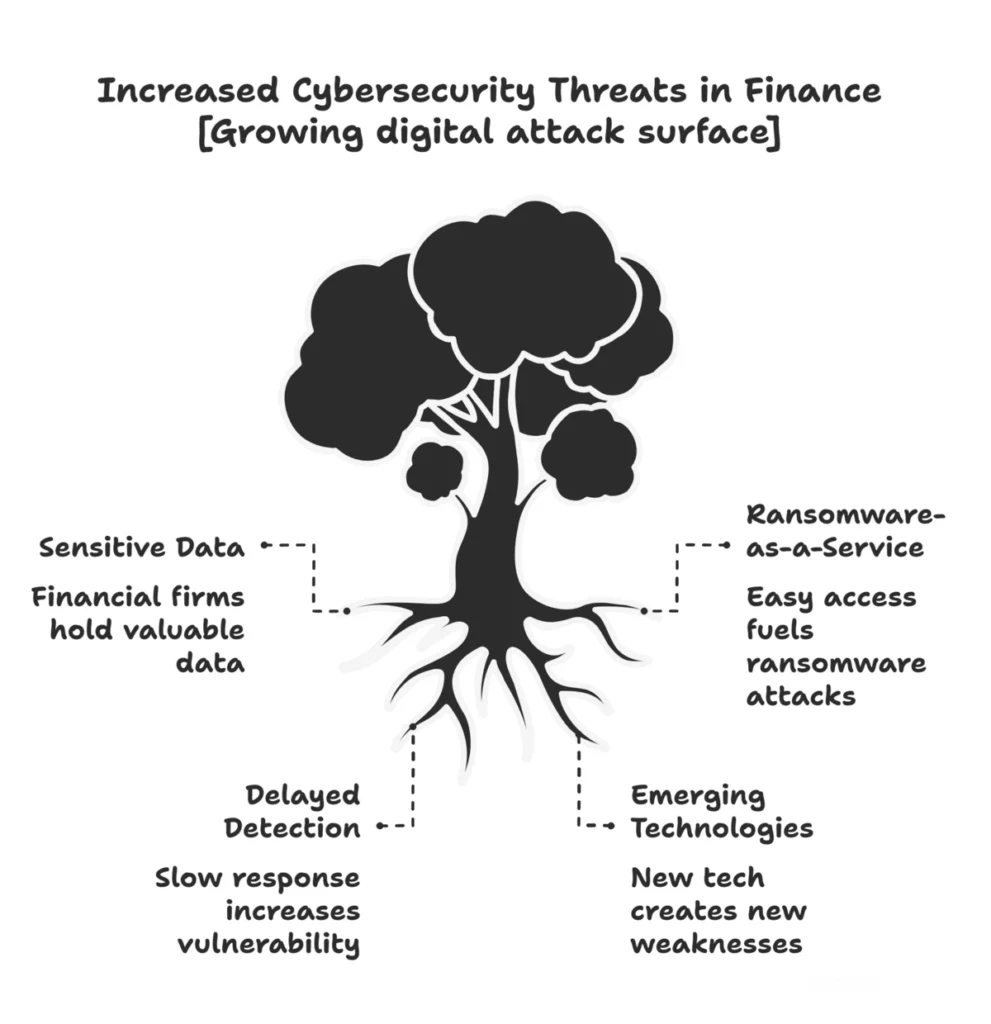
Financial institutions have huge tracts of sensitive data, account numbers, social security number, transaction history and manage a powerful flow of money. This makes them a main goal for cyber criminals. Modern danger varies from ransomware to sophisticated fishing.
The “Ransomware Top threatening Vector” continued, which fuel was provided by easily utilizing the Ransomware-E-Service Tools kit. Criminals often combine strategy -for example, they use voice fishing and agree to circumvent business -post messages.
This increasing danger is not just theoretical. The IMF and the World Economic Forum emphasize that “cyber events can put operational flexibility and macro-financial stability in financial institutions” at risk. ” In practice, this means that a larger bank can cascade in a hack market panicies or liquidity crisis. Tireless attacks. For example, a study found that financial companies face the second most violation costs for any industry.
In 2024, financial companies took 168 days to identify an intrusion and on average 51 days to fix it. This is not about six months of attention. Although it is slightly better than other areas, it still leaves a lot of time for fraud and damage.
No wonder banks spend heavily on cyber security: Companies with dedicated events response teams save around $ 248,000 per year, and people with strong identity/access checks save $ 223,000 annually. Investment in AI and automation also pays: Companies using security AI cut BREECH costs with an average of $ 4.9 million. Cyber security is a dynamic race in finance. As the technology goes on mobile banking, cloud services, IT units and even cryptic cases, new weaknesses emerge. All of these signs point to the same fact cyber security is not just an IT problem, it is crucial to protect our financial economy.
Case Studies: Breaches in Financial Institutions
Events in the real world bring home why strong defense means something. In 2024, several major financial breaches came and highlighted the data to millions.
A dramatic example was the Landepot Brech. Landepot was infiltrated by hackers (Alphv/Blackcat Gang) in January 2024 – a large American pledge – and stole the customer files. The attack exposed names, addresses, financial account numbers and other PII for 16.9 million customers.
Landepot systems were cried for about two weeks. The incident showed how easily the credit and hostage companies can be affected, leaving customers at risk of identity theft.
Similarly, Evolve Bank and Trust Brech, in mid-2024, looked at 7.6 million people. Hackers stole the name, social security number, date of birth and account number. Lockbit assumed the responsibility and even incorrectly proudly said that data U.S. comes from the Federal Reserve.
In both Loandepot and Evolve cases, personal financial information about customers was exposed to the scale, where there was confidence in digital bank partners.
Credit associations and insurance companies have also suffered losses. Patelco Credit Union Ransomware Attack (mid-2023) stopped online banking for half a million members. Later, it was discovered that data from 1 million people were compromised (name, SSN, etc.).
Similarly, Prudential Financial revealed a violation of a 2.5 million client at the beginning of 2024. In each case, banks and insurance companies strolled to inform the victims, offer credit monitoring and increase security. These examples emphasize a main point: No companies are immune. Whether it is a community bank, Fintech partner or credit association, attackers are aimed at systems with financial data. Each offense performed large costs – not only cleaning fees but also iconic damage and legal fall. Customers can leave and new rules may come. Stories of Landepot, Evolve and others are careful stories that show that cyber security should be active, not reactive.
Leveraging AI and New Technologies
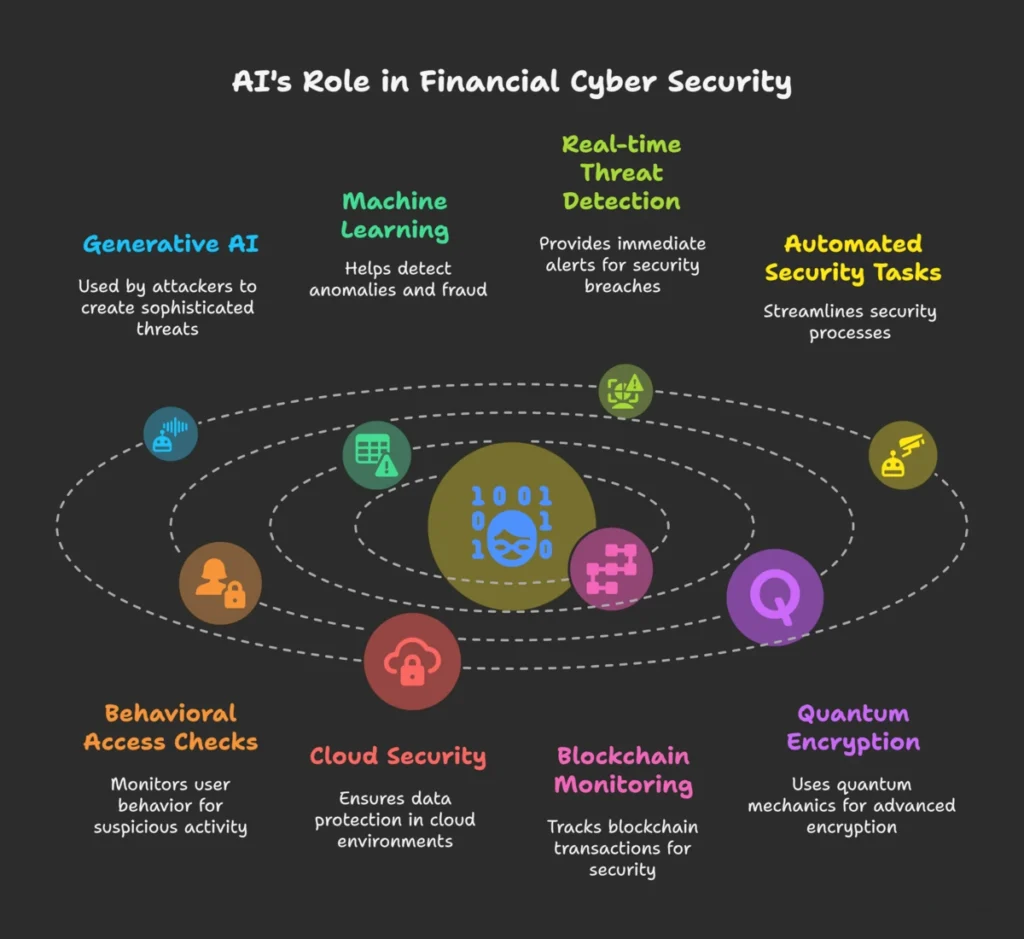
New technologies will challenge and help financial cyber security. On the one hand, Anti -i, blockchain utilization and quantum calculation will utilize the effort to crack encryption. On the other hand, guards have powerful equipment available.
Generative AI:
Generative AI changes cyber security. Malicious actors can use it to create highly secured fishing -post messages or deepfake voices, making social engineering more effective social technology. AI-augmented social engineering is ready to become a top threat. In fact, the attackers already use AI to “mutate malicious codes in real time” and adapt malware on the go.
However, cyber security teams can turn the table with AI. Machine learning algorithms can detect deviations in transactions or log into behavior much faster than humans. The banks are deployed to AI to scan millions of transactions for scam indicators and to follow the attack landscapes in the “Red Team” practice. Recent IBM reports found that organizations that use AI and automation in safety saved on average compared to those compared to $ 2.22 million per Breech. In other words, AI is not just a risk – this is a strength multiplier.
How AI Shapes the Future of Cyber Security in Finance
AI changes financial cyber security with smart tools such as real-time hazards, automated security tasks and behavioral access checks. Banks use AI to detect fraud and generate fake data to train and scan the rules.
As threats develop, trends such as cloud safety, blockchain monitoring and quantum saffron encryption are needed. However, experts have warned that only 24% of generic AI projects are safe. For strong security, financial companies should combine AI innovation with a strict security regime. The future future depends on smart, AI operated cyber security.
In the cyber security business
Focusing all this on finance and technology means that talent is in great demand. “Cyber security is a good career for individuals?” – Answers are a great yes, especially in finance. Cyber roles in banks and fintech pay well, often over other industries.
According to industry data, an American cyber security analyst earns an average of $ 75,000- $ 105,000 (entry-level roles start from $ 70- $ 80k and grow rapidly). Up to the middle of their career, analysts can earn 100,000 dollars- $ 150,000.
Senior items pay even more: Chief Information Safety Officers in Finance often earn 160,000 dollars- $ 250,000 or more. In fact, fields such as finance and authority place “a premium on cyber security wages due to the sensitive nature of the data.”
Why so high wages? Supply and demand. The World Economic Forum is estimated to have a global lack of around 4 million cyber security professionals, and more than half of organizations cite skills as their biggest cyber challenge. This difference is particularly pronounced in finance, where compliance requirements (GDPR, PCI-DSS, PSD2, etc.) force banks to hire more experts.
What does a cyber security analyst do? In financial services, analysts monitor networks, systems and transactions for suspicious activity. They also help to educate employees (for example, by running phishing simulations) and respond to incidents, coordinating with law enforcement and observation teams.
How to go to this field? Begin with a strong foundation: degrees in computer science, information protection or design are common. But many professionals also come from self-study or boot camp. Online courses and certificates are important. For example, the Cyber Security Professional Certificate of Google and Isaca (ISC), Cisco or CompTIA are recognized. Financial companies often seek certificates such as CISSP, CEH or CISM, plus special skills (cloud safety, data analysis).
Mentorship and social assistance. A cyber security hub or a professional group (events such as online forums, local ISACs, and financial cyber practice) creates contact and keeps the skills sharp. Banks or fintechs have an internship Golden – many companies run internships for cyber security or rotation programs.
Conclusion:
Future of Financial Security
The financial world has become more digital, mutually linked and complicated. As it does, cyber security will only increase in importance – this is the future of financial security. The company that invests in defense (AI equipment, skilled team, zero-confidence architecture) will reduce losses and gain confidence. Supervisors and companies all over the world already transfer budgets and strategies for cyber flexibility and accept games.
For professionals and new people, there is an exciting field: the demand for talent, the speed of innovation and the important missions of money protection all promise a dynamic career. For consumers, it means better-protected bank apps and security (with intelligent practice on their behalf). And for the global economy, this means a safe base for development in innovation time.
When we look forward to 2025-2030, one thing is clear: Cyber attacks will develop in financial services, but we will be defended. Either your organization – or you, as part of the workforce – be prepared to fulfill the next danger? What steps will you take today to ensure a safe financial future?